Production Of Transgenic Animals Notes

Advantages of Transgenic Animals.
Production of transgenic animals notes. The main principle in the production of transgenic animals is the introduction of a foreign gene or genes into an animal the inserted genes are called transgenes. PowerPoint PPT presentation. A transgenic animal is an animal in which one or more genes have been introduced into its nonreproductive cells.
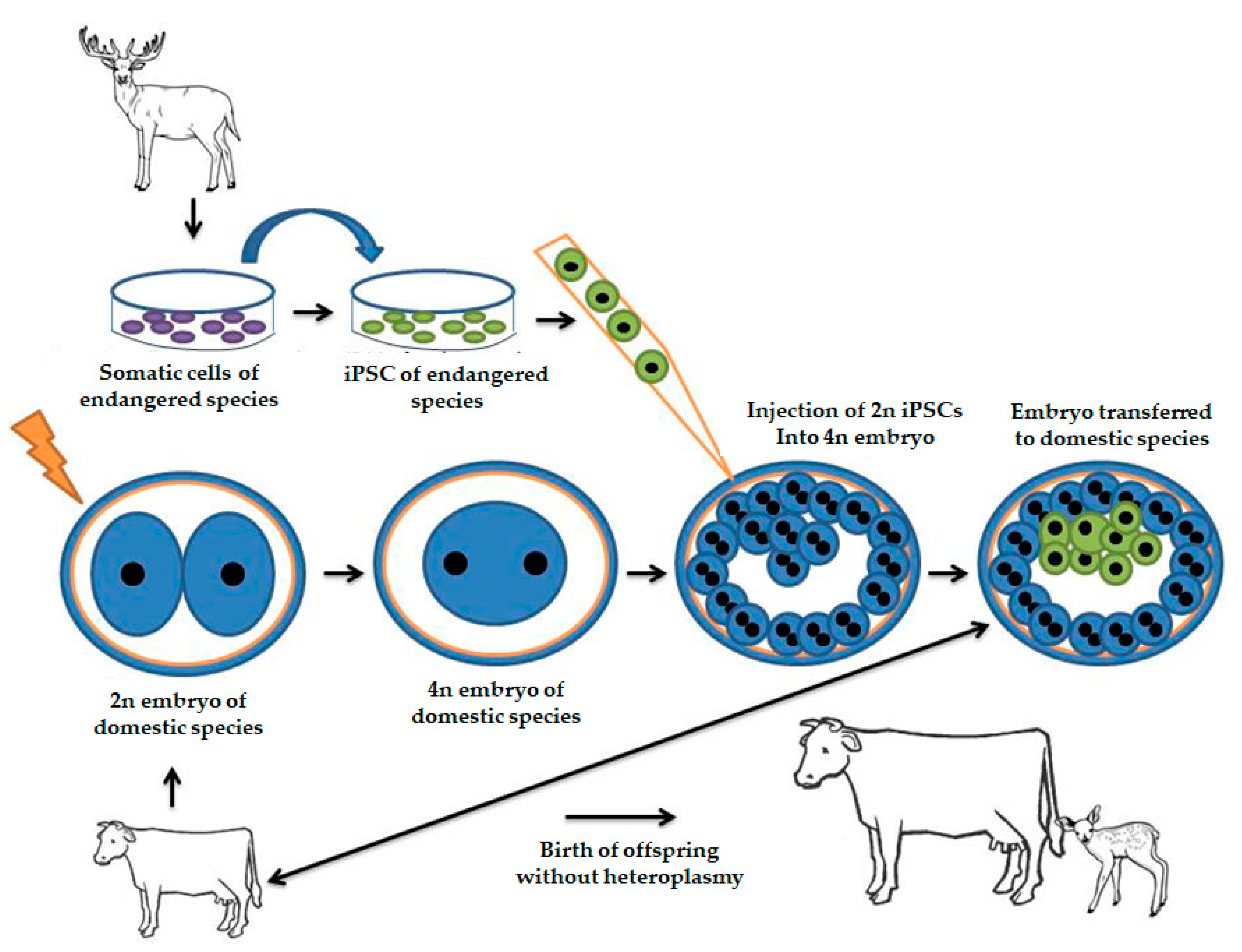
One favoured method involves the inoculation of the DNA into the pronucleus of a fertilised ovum followed by implantation into pseudo pregnant females. Microinjection blastocyst injection and using a retrovirus Nuclear transfers Artificial chromosomes for gene transfer PRODUCTION OF TRANSGENIC ANIMALS THE METHODOLOGY. Transgenic animals are used as tools in research and for the production of recombinant proteins The main applications of transgenic animals are described as follows.
The animals used for transgenic purpose naturally carry the mechanism needed to produce complex protein. Agricultural Applications a Breeding Farmers have always used selective breeding to produce animals that exhibit desired traits eg. 43 Creation of the transgenic animal A number of methods are currently in use for the creation of transgenic animals.
Studying gene function. A Gene requires certain cellular mechanism to help for the production of protein. The development of transgenic animals has been part of biotechnology research which has been expanding rapidly.
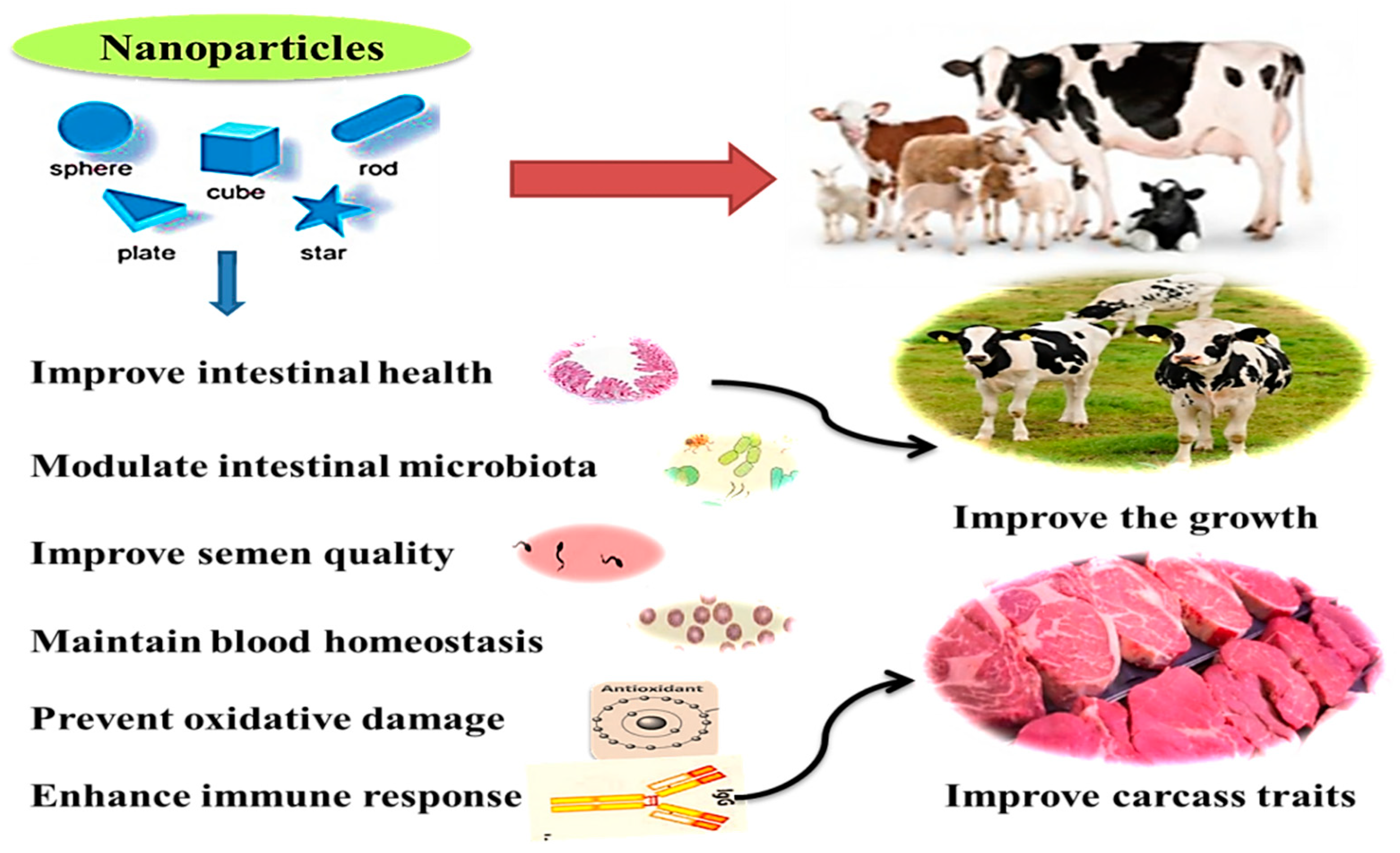
Trans-genesis is important for improving the quality and quantity of milk meat eggs and wool production besides creating drug resistant animals. The foreign genes must be transmitted through the germ line so that every cell including germ cells of the animal contains the same modified genetic material. Let us discuss a few of them here.
Transgenic animal technologies have come a long way since the creation of the first transgenic mouse in 1974 Transgenic Mouse 2005. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. To yield industrial as well as consumer product To research human diseases To produce pharmaceutical products and tissue for implantation.