Marine Animals Definition Biology

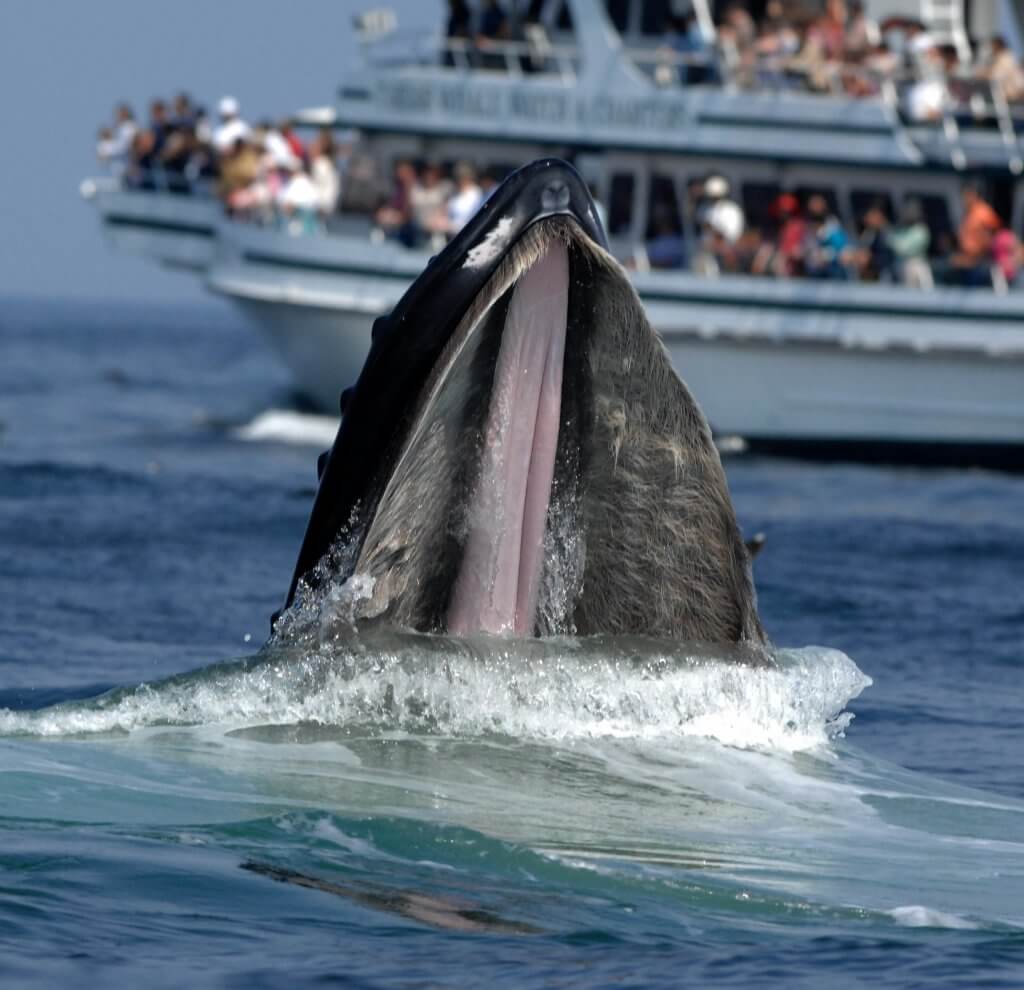
Marine biology is the scientific study of plants and animals that live in salt water.
Marine animals definition biology. Given that in biology many phyla families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Marine biologists may have many different jobs including working with marine mammals eg a dolphin researcher studying the seafloor researching algae or even working with marine microbes in a lab. Spongin- flexible protein fibers.
It also deals with airborne and terrestrial organisms that depend directly upon bodies of salt water for food and other necessities of life. Earth is often referred to as the blue planet because seas and oceans cover more than 75 of the Earths surface. Marine biology is the study of marine organisms their behaviors and interactions with the environment.
Marine biologist definition is - a scientist who studies life in the sea. Marine biology is the study of marine ecosystems marine organisms and human interactions with these environments and species. Look it up now.
Marine life definition biology. An animal belonging to the mammalian order Sirenia which includes manatees and dugongs. Marine biology synonyms marine biology pronunciation marine biology translation English dictionary definition of marine biology.
Spermaceti is found in a cavity in the head of sperm whales. Osculum- large opening that lets water out. The scientific study of organisms living in or dependent on the oceans.
Collar cells- create moving force in a sponges body. A thin colorless transparent oil that forms a waxy material when it comes into contact with air. Marine biologists study biological oceanography and the associated fields of chemical physical and geological oceanography to understand marine organisms.