Deep Ocean Animals Adaptations

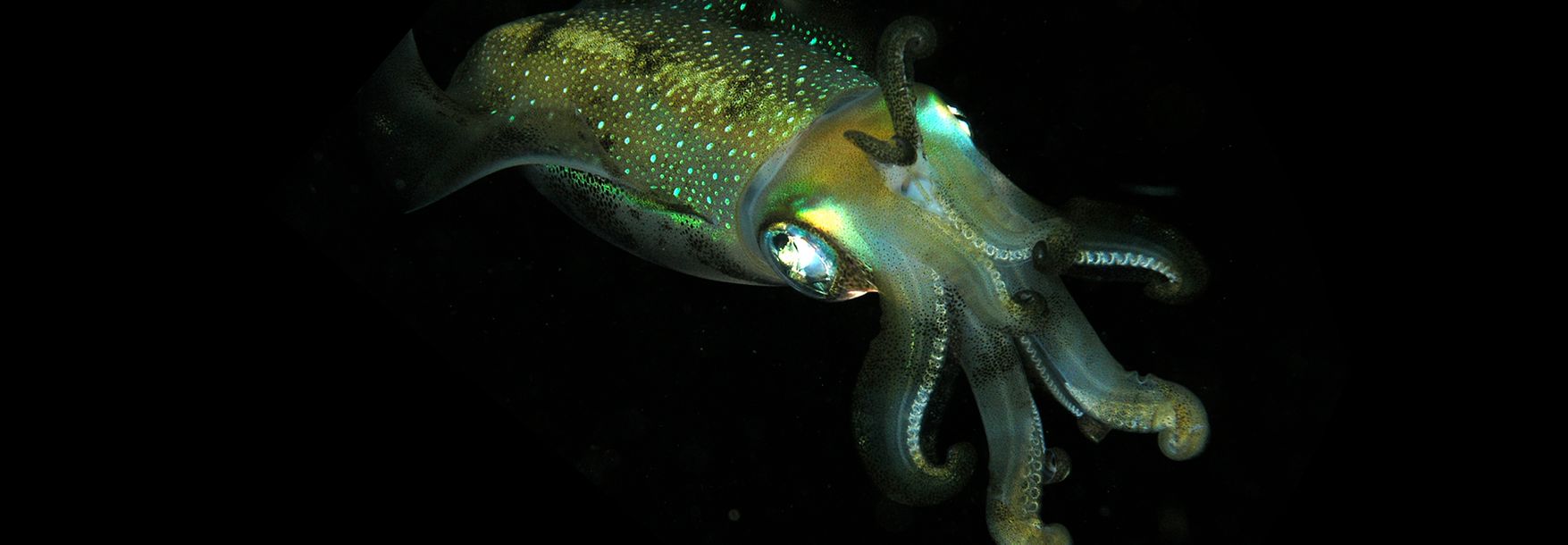
But deep ocean animals such as this Barreleye fish have evolved excellent eyes for seeing in near-total darkness.
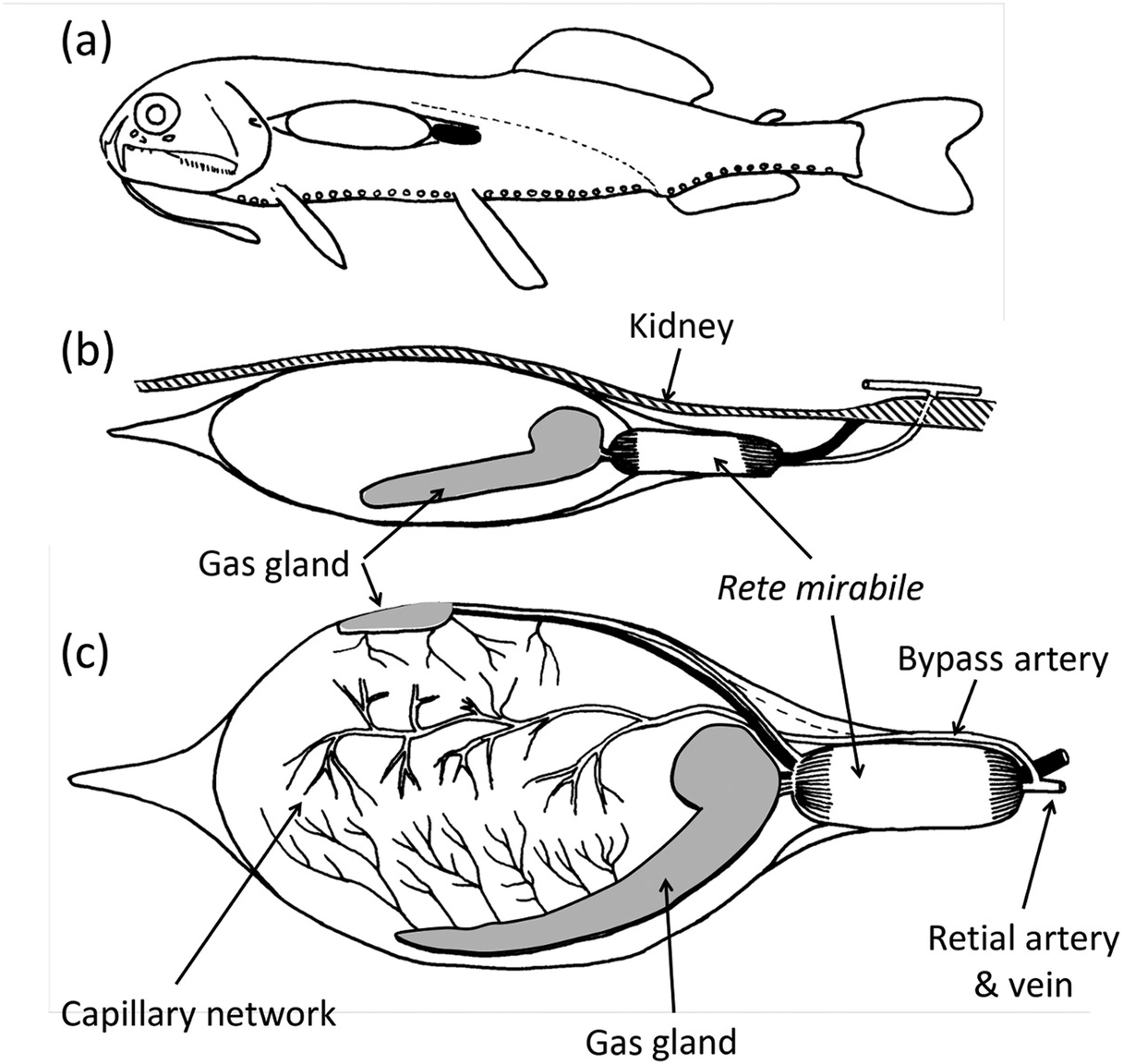
Deep ocean animals adaptations. 4000 m 6000 m and Hadal from 6000 m and below zones Pelagic division includes Mesopelagic 200. Water depth temperature and the presence or absence of light are some of the conditions that differ in these habitats. These creatures have several adaptations like compressible lungs lung-like swim bladders etc to help them overcome the high water pressure in their deep-water environment.
Coastal plants need special adaptations to survive. Introduction to Deep Sea Adaptation. Animals adapt to their environments to help them survive.
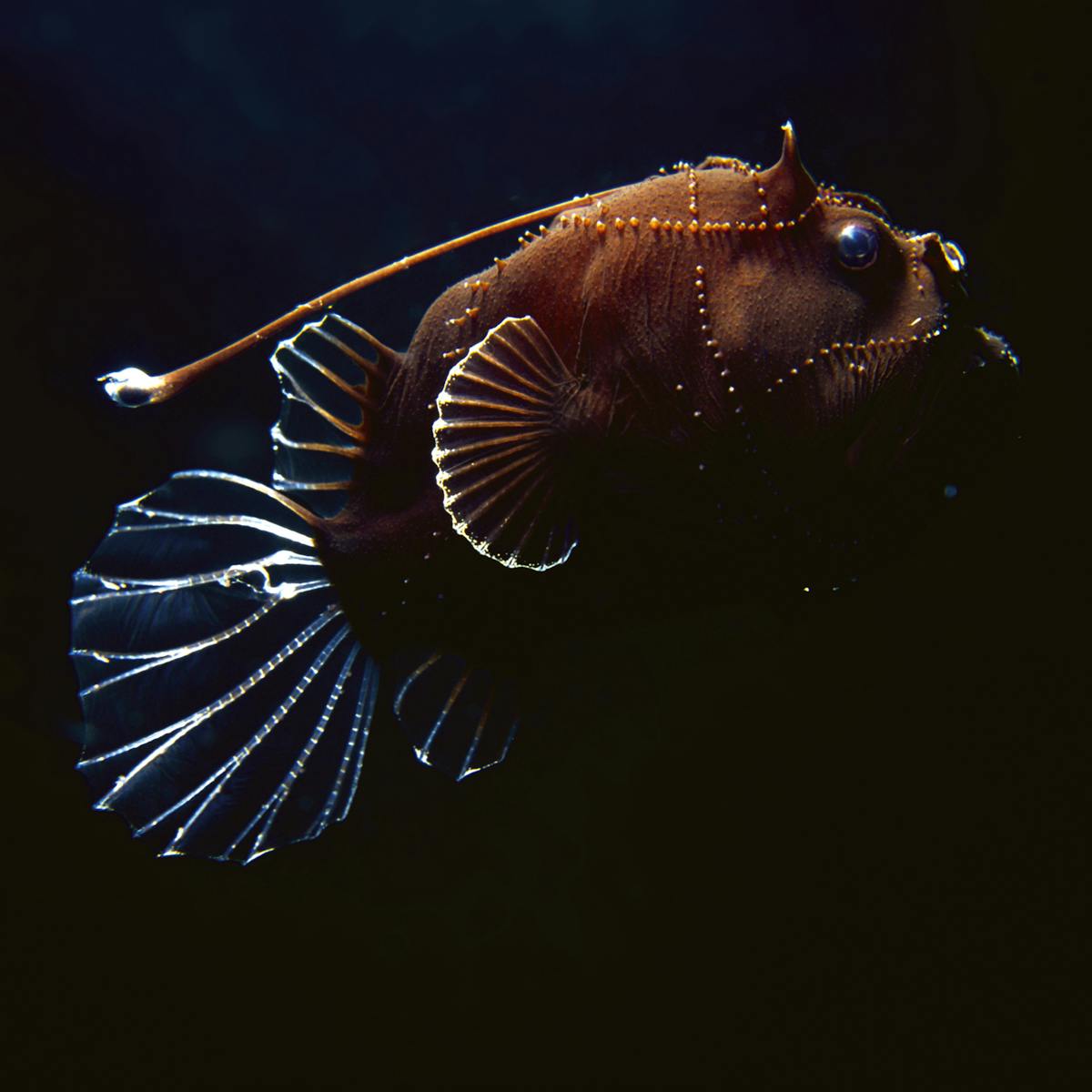
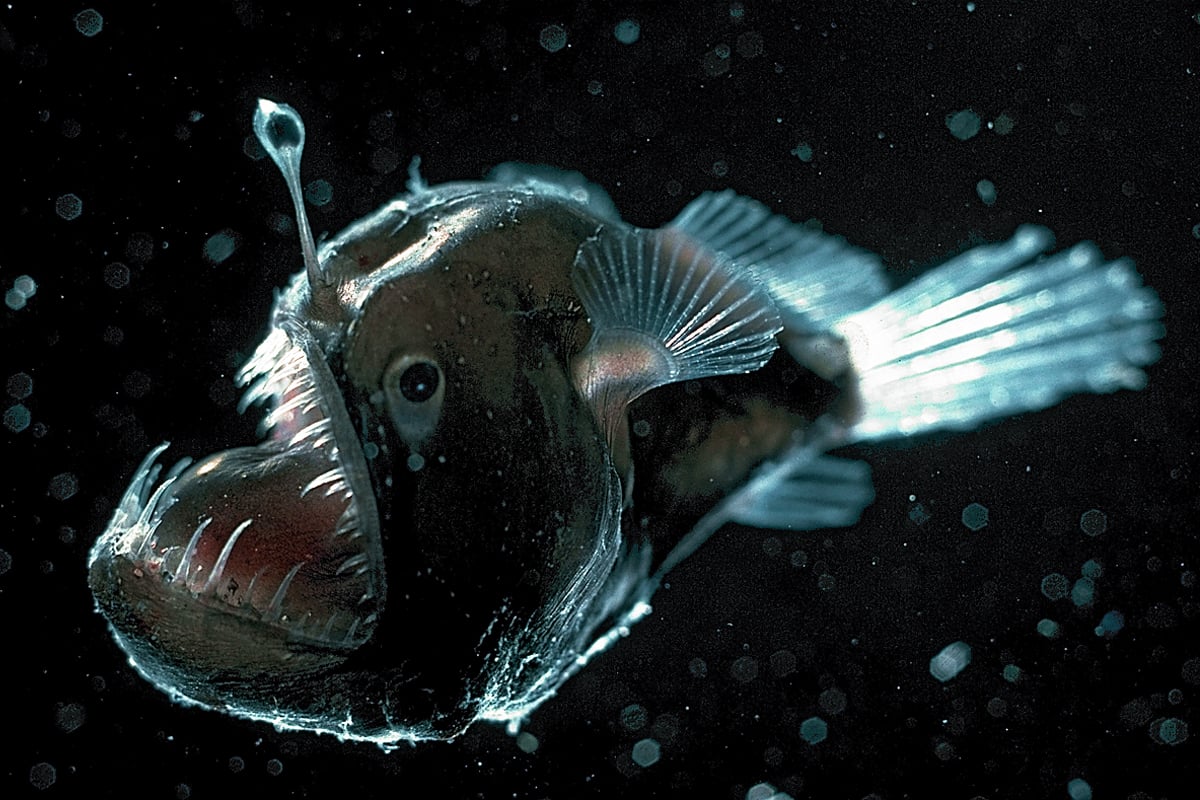
Connection to NGSS -. Sharks are very good at finding food. In anglerfish Linophryne Fig 24 the light is used as a.
Deep-sea creatures are animals that live below the photic zone of the ocean. Deep Ocean Animal Adaptations These lessons are part of a deep ocean unit. Childress T he deep ocean is unlike terrestrial and shallow en- vironments in many ways but two of the most im- portant are its vast scale as a habi- tat and the pervasiveness of con- ditions throughout it.
Why are deep sea creatures. Watch a recording of this video webinar. The deep sea is not only under a lot of pressure but it is also very dark.
Rods help eyes sense light. In some other deep-sea fishes eyes are very small as they are of little apparent use and still others are without eyes. In future lessons students will research rocky shore animals to compare animals in these 2 habitats.