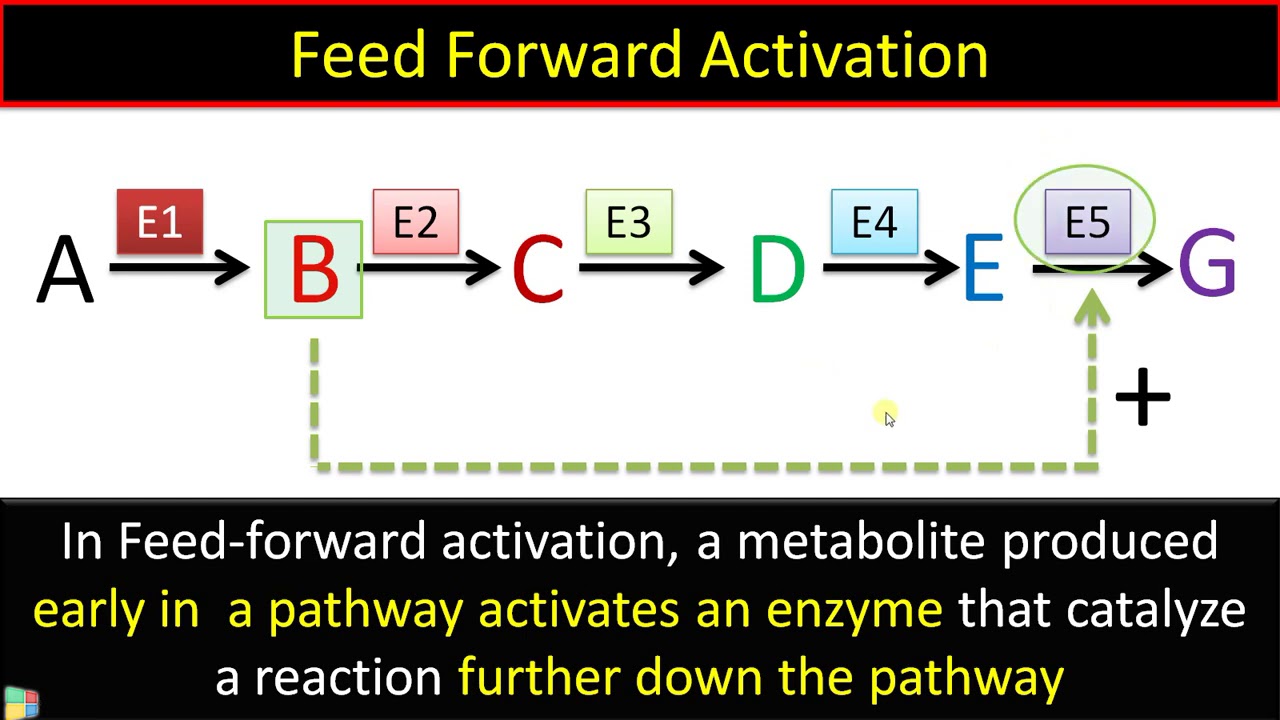
Cellular Respiration Equation Explained

Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy.
Cellular respiration equation explained. Nutrients are needed for cellular respiration. At the end of the electron transport chain oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. Such processes are explained below.
Cellular respiration can be summarized as glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water atp energy cellular respiration in plants. Glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water energy The equation is formulated by combining the three following processes into one. The energy released from the broken down molecules are a result of spontaneous catabolic reactions.
Cellular respiration is the process by which food in the form of sugar glucose is transformed into energy within cells. This process occurs in the mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products.
Cellular Respiration gives both plant and animal cells the useable energy aka ATP that they need to do stuff. Cellular respiration is a common process that is carried out by many organisms to make and release energy. C6H12O6glucose 6O2 6CO2 6H2O 38 ATP.
C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O Energy as ATP The word equation for this is. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 38ATP Glucose 6 Oxygen 6 Carbon Dioxide 6 Water ATP. But the last two steps the Krebs cycle and ETC happen in the mitochondria.
This is the balanced equation that yields energy. Glucose oxygen chemical energy carbon dioxide water Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create atp a chemical which the cell uses for energy. Cellular respiration formula explained.