Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

Contains chromosomes DNA code for the synthesis of proteins that control the function of the cell hence the nucleus commands the cell Cell Surface membrane.
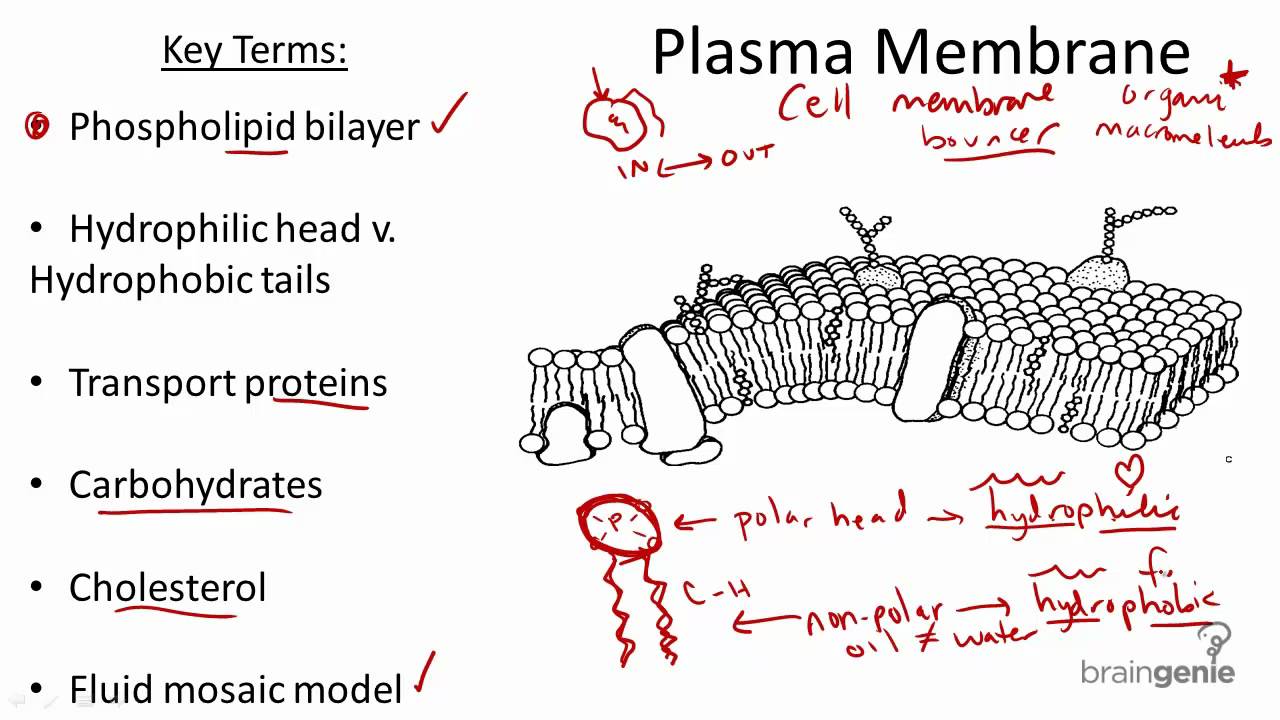
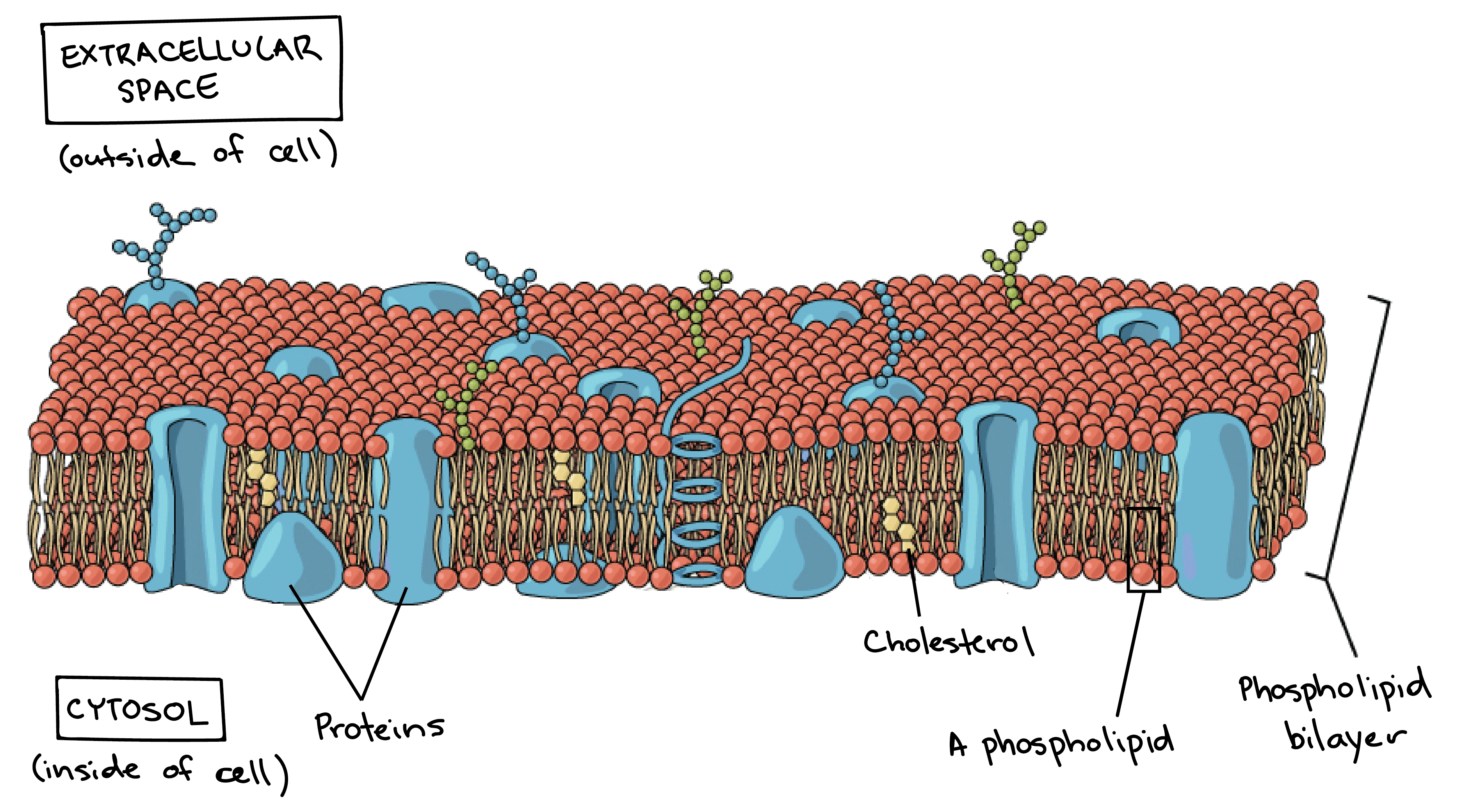
Cell membrane structure and function a level. Different organelles have distinct structures and functions. Formed from a phospholipid bilayer with the hydrophobic tails pointing towards each. Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane.
The membrane is examined in detail later. This structure can even be called the inner membrane to distinguish it from the outer membrane present in gram-negative bacteria. 1 Isolate cells contents from outside environment 2 Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3 Communicate with other cells Note.
This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. Membranes are selectively permeable so are effective barriers in controlling what goes in and out of cells. The fine detail of the cell which may be revealed by an electron microscope is called the cells ultrastructure.
These structures are called Organelles. Xylem present in the vascular plants is made of cells that provide structural. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes.
Organelles perform different functions within a cell and this is called the Division of Labour. Membranes also exist within cells forming various. The Formation of Cell Membranes is Crucial to Life.
Organisms are composed of cells and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment which protects the cell from its environment. -A double membrane sac which pinches off the end of organelles such as the RER or Golgi Apparatus and fuses with other membranes such as the RER Golgi or Plasma Membrane Function of Vesicles -Transport proteins and other substances between organelles and the outside of the cell.